1599 Geneva Bible (GNV)
The Geneva Bible: A Cornerstone of English Protestantism A Testament to Reform The 1599 Geneva Bible... Read More
Urartu was a mountainous region and is largely the territory of modern Armenia. Known in the Scriptures as "Ararat, Minni and Ashchenaz"' (Jer. 51:27). It's borders ran on the north by the Caucasus Mountains; on the east by Media and the the Caspian Sea; on the south by Media and Assyria, and on the west by the Euphrates River. It was the source for four mighty rivers: the Araxes, the Tigris, the Euphrates and the Acampsis. The ark of Noah rested on the top of one of the mountains of the Ararat mountain range. Within the borders some believe the Garden of Eden was situated.

- Arame (Armenian) (ruled 858-844 BC) was the first known king of Urartu.
- Arame lived during the time of King Shalmaneser III of Assyria (ruled 859-824 BC).
- Arame united the Nairi tribe against the threat of the Assyrian Empire.
- Arame's capital at Arzashkun was captured by Shalmaneser.
Media played an important role in Old Testament times. They were a mountainous region with its boundaries at the Araxes River and Caspian Sea on the north; the Great Salt Desert of Iran on the east; Persia on the south, and the Zagros Mountains on the west. in 633 BC the kingdom of Media was established, and soon overpowered Assyria, Armenia and Persia, and formed the Medo-Persian empire, which conquered Babylon in 536 BC. After this the history of Media was intermingled with that of Persia.
Phraortes King of Media 522 BC

- Media was the Madai of the Hebrews.
- Media was located NW of Persia and south of the Caspian Sea.
- The territory of Media was 150,000 square miles. - The Medes were actually one of the most powerful nations of western Asia.
- They were descendants of Japheth.
- Media ruled over Babylon from 2458-2234 BC and occupied a tributary place until 880 BC, when they revolted from Assyria.
- The Median empire was at its height in 625 BC and was conquered by the Persian king Cyrus in 536 BC. and the Medo-Persian empire was founded, which lasted until the conquest of Alexander the Great in 330 BC. See Isa 13:17; Est 1:19; Dan. 6:8-12; 1 Chron. 5:26.
Persia played an important role in Old Testament times. Originally a small province on the Persian Gulf, still known as Fars; but Persia proper included, besides the sandy plain on the Gulf, a mountainous plateau north of it, and was bounded by Media on the north; by Carmania on the east; by the Persian Gulf on the south, and by Elam on the west. The Persian empire rose to greatness at the fall of Babylon in 536 BC; they conquered and ruled over all the lands from India to Ethiopia, and was by far the greatest of the Oriental monarchies. The capital was Susa, called in the Bible Shushan, The Palace (Esther 1:2), was not in Persia proper, but in Elam. Persia was overpowered by Alexander the Great in 330 BC.
Darius 1 "The Great" Seated on his Throne
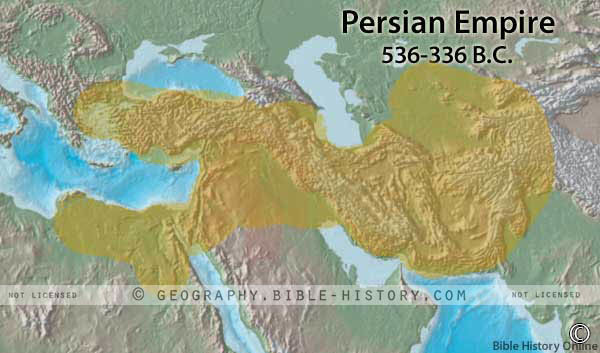

- Originally Persia was the country around the head of the Persian gulf, but later became that great empire which extended from India to Egypt, and included all Western Asia south of mountains.
- The Persians and Medes were of the Aryan stock, from the line of Japheth.
The highest Persian god 'was Mithra, "the sun" deity.
- The kingdom of Persia reached its height under Cyrus the Great who reigned from 559-529 BC, and his successors, to the time of Xerxes 486-465 BC.
- Persia fell under the victorious arms of Alexander in 330 BC in fulfillment of Bible prophecy.
The modern name of ancient Assyria is Kurdistan. Its territory was lying on the western slope of the Zagros mountains, and extending across the Tigris to the Sinjar hills and border of the Mesopotamian desert. The Assyrian kingdom began about 1273 BC, around the same time as the Judges of Israel The earliest capital was Kileh Sherghat ; afterwards the seat of government was moved to Nimrud, and finally to Nineveh, the centre of the great Assyrian Empire, which at one time conquered almost all the lands of the east.
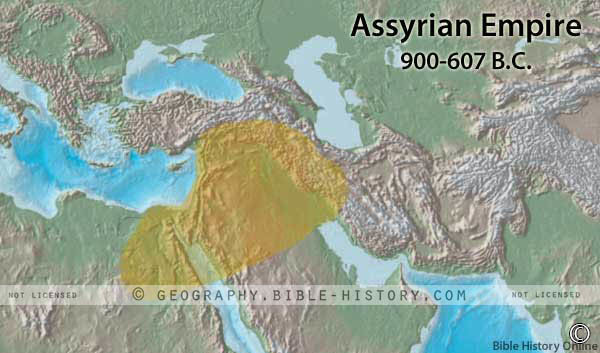
- Assyria was located on the Tigris (Gen. 2:14) with its capital at Nineveh, Gen. 10:11.
- Assyria got its name from Asshur, the son of Shem, who they worshipped as the chief God.
- At the height of Assyria's power it included Susiana, Chaldea. Babylonia, Media, Matiene, Armenia, Assyria proper, Mesopotamia, Syria, Phoenicia, Israel and Idumea.
- The Assyrian people were originally from Babylon, they were the descendants of Shem
- Assyria flourished for over 500 years, and fell a prey to the revolting Medes in league with the Babylonians in 625 BC.
Isaiah prophesied Assyria's destruction, Isa. 10:5-19. See also Ezek. 31.
The country southeast of Assyria and west of Media and Persia, between the Zagros mountains and the Tigris river. Shushan, or Susa, the capital of the Persian Empire, was actually the chief city within this province.
Funerary Head of an Elamite

- Elam was a son of Shem, Gen. 10:22, and the country peopled by his descendants, Gen. 14:1-9.
- Originally Elam was a portion of Lower Mesopotamia, which Babylon was a part, but afterwards Elam became a dependent of Persia.
- Shushan (Susa) appears to have been part of Elam, Dan. 8:2.
The word Mesopotamia means "between the rivers," and in the Bible the name was usually applied to the whole plain between the Tigris and the Euphrates, including even Chaldaea and a part of Assyria. Throughout time the name Mesopotamia became associated with the northwestern portion of the region between the rivers, above the area where they almost meet. Haran, the home of Abraham's family, and the native place of Rebekah, Rachel and Leah, was a part of Mesopotamia.
Seated Statue of Gudea, Prince of Lagash, Mesopotamia

- Paddan Aram where Jacob fled to was part of Mesopotamia, because he had family there.
Chaldaea was the land of Shinar and Babylonia. Its territory was mainly the city of Babylon and the southern portion below Babylon. Within its borders the Tower of Babel was erected, and a man named Nimrod founded the earliest empire in history. Within the province of Chaldaea was the city of Ur, the dwelling place of Abraham, the first Hebrew. The chief city of Chaldea was Babylon, which became the capital of the great Babylonian Empire, and the greatest city in the East.
The country lying along the Euphrates, on both sides, and between it and the Tigris for a distance of three or four hundred miles back from their mouths. But in a general sense made to include Babylonia.
- The soil of Chaldaea was similar to the Nile.
- The area comprising ancient Chaldaea is now dotted with mounds, which are the ruins of large cities.
- The Chaldaeans, who, by the time of the Captivity of Judah, constituted the learned classes, the philosophers, magicians, and advisers of Babylon, and a language which was impressed on Babylonian literature, Dan 5:30; Dan 9:1
The land of Egypt was also referred to in Scripture as "Mizraim," "Rahab," and "the Land of Ham." It is situated in the northeastern corner of Africa, and its boundaries are the Mediterranean Sea on the north; and on the east by Israel, the Arabian Desert and the Arabian Sea, also known as the Red Sea; on the south by Nubia, and on the west by the Great African Desert. Its luxurious river is the Nile which has its sources in Central Africa, and flows northward into the Mediterranean Sea. Egypt ruled as a kingdom for many centuries, it was the land in which Israel was made slaves and held in captivity. The history of Egypt is connected with many other events in Bible history.
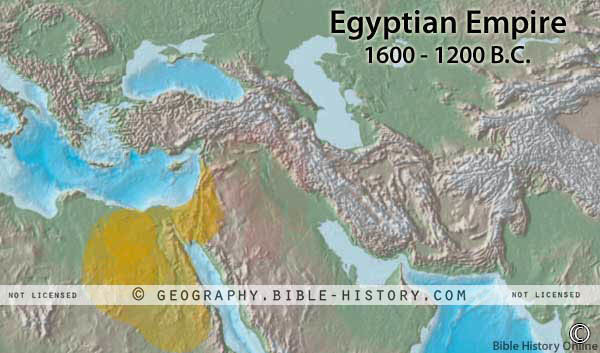
- The northeasternmost country of Africa, fronting the Mediterranean.
- Egypt is the Greek and Roman name for it, and probably signities "land of sunshine." - The Hebrews called it Mizraim, the son of Ham, Gen. 10:6.
- It is also called the Land of Ham" in Ps. 23:27. - Its Arab name is Mizr, "red mud," which is the equivalent of Mizraim.
- Its Egyptian name is Kem, "chem," "black," equivalent of Ham.
- Egypt's most attractive feature is the Nile and its fertile valley.
- Egypt's fertility, dense population, arts, sciences, literature, and religion gained attention from the earliest of times.
- The Jewish empire and people reflected the learning and customs of Egypt.
Meaning - fire, light, valley. Ur was the country of Terah and birthplace of Abram ; called ** Ur of the Chaldees," Gen. 11:28; 15:7. The Jews identify it with Orfah in Mesopotamia.
BABEL or BABYLON (confusion). Capital city of Shinar or Chaldea. The tower of Babel (Gen 11:4, 5) is regarded as the primitive site of the city. Babylon lay on both sides the Euphrates. It was the grandest and most populous city of ancient history. The kingdom was begun by Nimrod, Gen. 10:6-10. It fell under Persian influence, BC 555, and in the manner described by Jer. 11:31; Isa. 21:10 ; Dan. 5:30. Babylon in Rev. 14:8 represents Rome, as an element antagonistic to the Jews. See Illustrated Bible History - bible-history.com/ibh
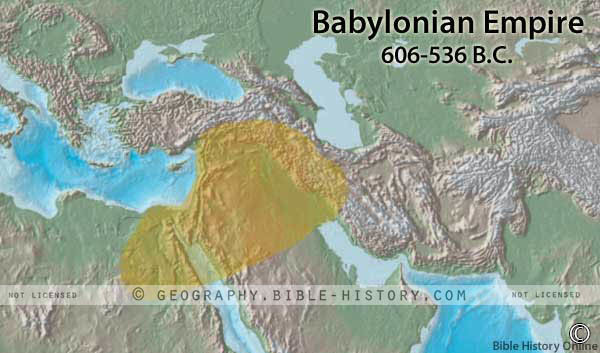
Babylonia (pronounced babilahnia) was an ancient empire that existed in the Near East in southern Mesopotamia between the Tigris and the Euphrates Rivers. Throughout much of their history their main rival for supremacy were their neighbors, the Assyrians. It was the Babylonians, under King Nebuchadnezzar II, who destroyed Jerusalem, the capital of the Kingdom of Judah, and carried God's covenant people into captivity in 587 BC. The Bible reveals much about the Babylonians all the way back from the time of Hammurapi (2000 BC) to the fall of Babylon (about 500 BC). Throughout the Old Testament there are references to the Babylonians, their people, culture, religion, military power, etc.
Babylonia was a long, narrow country about 40 miles wide at its widest point and having an area of about 8,000 square miles. It was bordered on the north by Assyria, on the east by Elam, on the south and west by the Arabian desert, and on the southeast by the Persian Gulf.